Recently as per the new education policy,Design thinking has been added as a skill based subject for the students of CBSE board.
Design Thinking is a powerful, human-centered approach to problem-solving that encourages creativity, collaboration, and innovation. Integrating Design Thinking into secondary school curricula can equip students with essential skills for the future, such as critical thinking, empathy, and resilience. Here’s a detailed plan for implementing Design Thinking as a new skill subject for secondary school students as per NCERT syllabus.
Objectives
Foster Creativity and Innovation: Encourage students to think outside the box and develop original solutions.
Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Equip students with a structured methodology to approach and solve complex problems.
Enhance Collaboration: Promote teamwork and the value of diverse perspectives.
Build Empathy: Teach students to understand and address the needs and experiences of others.
Encourage Resilience: Help students learn to iterate and improve upon their ideas through feedback and failure.
Curriculum Outline
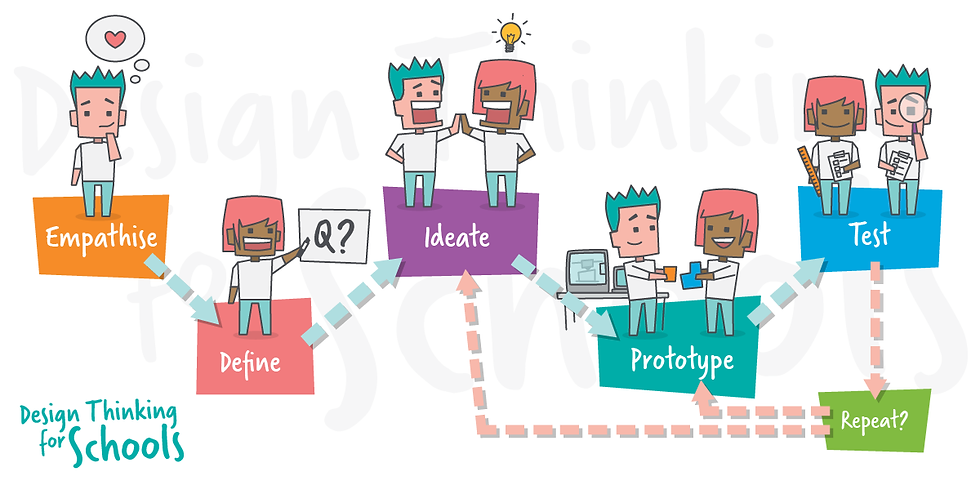
1. Introduction to Design Thinking
Overview: Introduction to the concept, importance, and stages of Design Thinking.
Activities: Interactive lectures, case studies of successful Design Thinking applications, and introductory projects.
2. Empathy
Understanding Users: Techniques for understanding the needs, motivations, and challenges of users.
Activities: Interviews, surveys, persona creation, and empathy maps.
3. Define
Problem Definition: How to articulate the problem based on insights from the empathy stage.
Activities: Problem statement workshops, "How Might We" questions, and collaborative brainstorming sessions.
4. Ideate
Generating Ideas: Techniques for brainstorming and generating a wide range of ideas.
Activities: Brainstorming sessions, sketching, mind mapping, and idea clustering.
5. Prototype
Creating Prototypes: Building tangible representations of ideas to explore potential solutions.
Activities: Rapid prototyping with materials like paper, cardboard, and digital tools, and creating low-fidelity prototypes.
6. Test
Testing Prototypes: Techniques for testing prototypes with users to gather feedback and insights.
Activities: User testing sessions, feedback collection, and iteration planning.
7. Implement
Bringing Ideas to Life: Steps to refine, develop, and implement the final solution.
Activities: Developing action plans, project management, and presentations to stakeholders.
Teaching Methodology
Project-Based Learning: Students work on real-world projects throughout the course, applying each stage of the Design Thinking process.
Collaborative Learning: Emphasis on teamwork and peer learning through group projects and activities.
Hands-On Activities: Engage students with practical, hands-on activities to reinforce theoretical knowledge.
Reflective Practice: Encourage students to reflect on their experiences and learnings at each stage of the process.
Assessment
Formative Assessment: Continuous assessment through class participation, group work, and regular feedback.
Summative Assessment: Evaluation of final projects based on creativity, problem-solving approach, collaboration, and implementation.
Resources Needed
Materials: Prototyping materials (paper, cardboard, markers, etc.), digital tools (software for design and prototyping), and access to user research tools.
Training for Educators: Professional development for teachers to effectively teach and facilitate Design Thinking.
Classroom Environment: Flexible spaces that encourage collaboration and creativity, such as movable desks and brainstorming areas.
Example Projects
Community Improvement: Students identify a problem in their local community and develop a solution to address it.
School Innovation: Students work on projects to improve their school environment or processes.
Global Challenges: Students tackle broader issues such as environmental sustainability or social justice.
Conclusion
Implementing Design Thinking as a subject in secondary schools can provide students with invaluable skills for their academic and professional futures. It promotes a proactive, empathetic, and innovative mindset, preparing students to tackle the challenges of the 21st century.
Kommentarer